What Wood to Avoid for a Chopping Board
Choosing the right wood for a chopping board is essential for both the longevity of your board and the safety of your food. While certain woods are ideal for cutting boards, there are several types you should avoid. In this article, we’ll discuss which woods are not suitable for chopping boards and why.
1. Softwoods (Too Porous & Weak)
Softwoods, such as pine, cedar, fir, and spruce, are not recommended for chopping boards. These woods are inherently soft and tend to develop deep grooves and scratches quickly from knife use. These cuts can trap food particles and bacteria, making them difficult to clean and posing potential hygiene risks. Additionally, softwoods absorb moisture more easily, leading to warping and cracking over time.

While softwoods may seem appealing due to their lower cost and availability, they lack the durability and resistance required for a high-performing cutting board.
2. Open-Grain Woods (Trap Bacteria & Moisture)
Wood with an open grain, such as red oak, white oak, ash, and mahogany, is also a poor choice for chopping boards. These woods have larger pores that can trap moisture, food particles, and bacteria. This makes them harder to clean thoroughly, which increases the risk of cross-contamination between raw meats and vegetables.
An open-grain structure can also lead to increased wear, as the fibers are more likely to break down under constant pressure from knives. Over time, this compromises the board’s integrity and can even make the surface rough, which is uncomfortable and inefficient for cutting.
3. Toxic or Allergenic Woods
Some exotic hardwoods can pose health risks when used for food contact surfaces like chopping boards. Woods such as walnut (though rare, it can cause allergic reactions in sensitive individuals), rosewood, wenge, and purpleheart should be avoided, especially if you’re not sure about their source or treatment. These woods can sometimes release toxic oils or chemicals that may affect the flavor of food or cause allergic reactions.
For instance, teak, while commonly used for outdoor furniture, contains natural oils that can dull knives and may impart an unpleasant taste to food. Certain woods, like rosewood or wenge, also have high silica content that can cause knives to lose their sharpness more quickly.

4. Oily or Resinous Woods
Oily or resinous woods, such as teak, eucalyptus, and cedar, are also not ideal for chopping boards. These woods have high levels of natural oils and resins, which can affect the food you prepare. Over time, these oils can build up on the board’s surface, making it difficult to maintain a clean cutting area. Furthermore, these woods may interfere with the seasoning process of your chopping board, as they prevent oil from soaking into the wood, which is necessary for proper board maintenance.
In addition, these oils can also make it harder to maintain a non-slip surface, which is crucial for safety when using a chopping board.
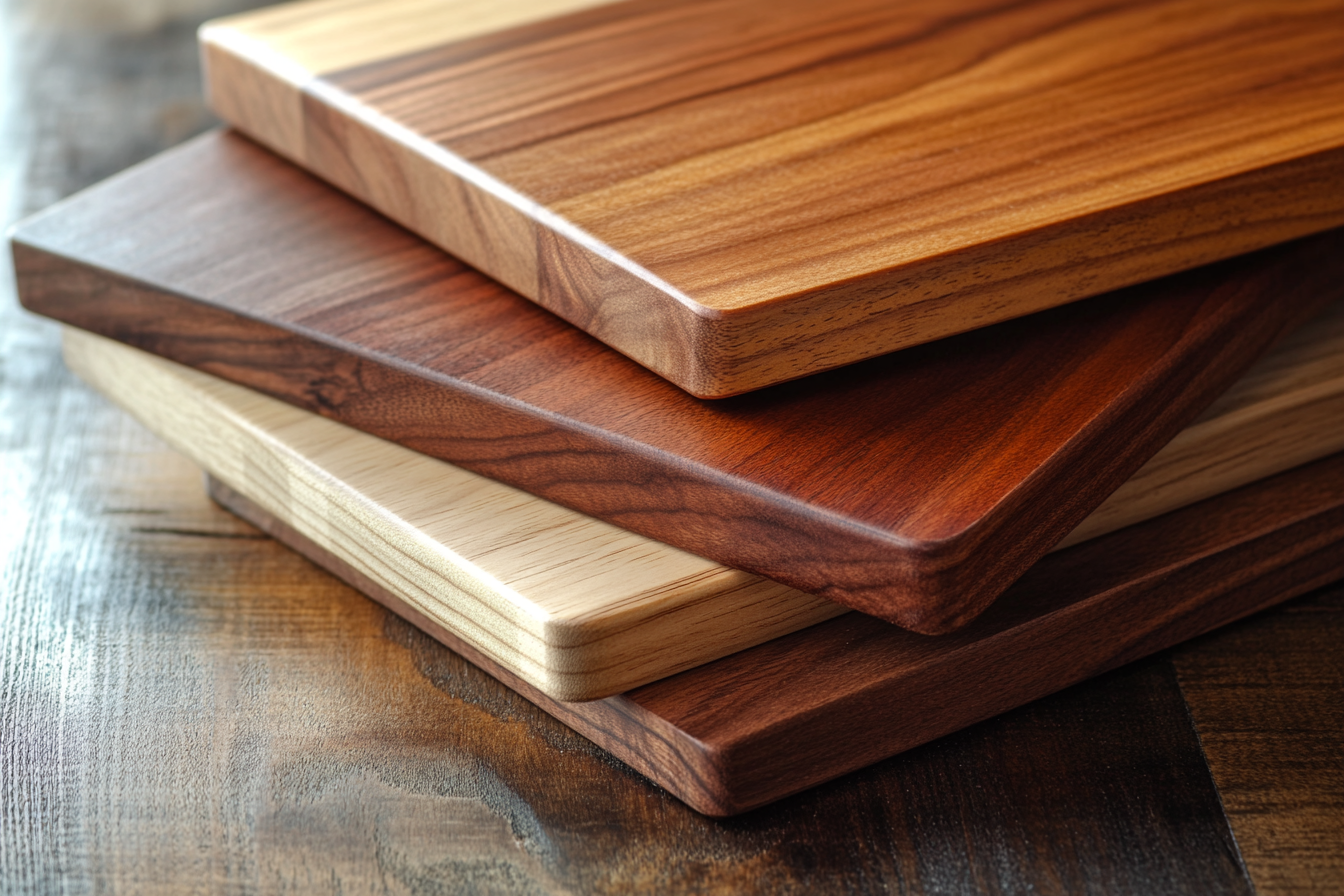
What Are the Best Woods for a Chopping Board?
To ensure both durability and hygiene, choose hard, closed-grain woods. These include:
- Maple (particularly hard maple or sugar maple) – Known for its durability, gentle knife-friendly surface, and fine grain.
- Beech – A dense, hard wood with a closed grain that resists scratches and absorbs minimal moisture.
- Walnut – A beautiful dark wood, resistant to moisture, and provides a long-lasting surface for heavy-duty use.
- Cherry – Offers both aesthetic appeal and strength, while being gentle on knives.
These woods are not only durable and knife-friendly but also relatively easy to maintain and clean.

Conclusion
While choosing the right wood for a chopping board is vital for both your kitchen’s hygiene and the board’s longevity, it’s just as important to avoid certain woods that can be harmful or inefficient for food preparation. Softwoods, open-grain woods, toxic woods, and oily or resinous varieties can pose problems like bacterial growth, warping, and knife damage. Instead, opting for hardwoods like maple, walnut, or cherry will ensure that you get a chopping board that lasts longer, performs better, and keeps your food safe.
If you’re shopping for a chopping board, be sure to look for quality hardwoods with tight, closed grains for the best experience!
This article aims to guide you on choosing the right material for your chopping board, ensuring it enhances both the safety and functionality of your kitchen.